Glossary
Two-Factor Authentication
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
-
Additional security for accounts, requiring a second authentication method for login.
With two-factor authentication, an additional method beside username and password is required to access an account. Usually this is through a mobile device, using for example a phone number or an app providing a verification code.
Accessibility Hint
- Accessibility Hint
-
Hints used to provide information about how an interface element works so everyone can use it.
An accessibility hint is additional information a user may need to interact with an element. You can think of it as instruction on how to use a control or button. This is particularly important for blind users, user with low vision, users with mobility disabilities and users with memory loss. Missing hints will make your app inaccessible for many users.
For some organizations, providing accessibility labels is mandatory, by law or by policy. In any case they are a good idea.
For example, you have an "Add" button that adds an item to a shopping basket. A good accessibility hint in this case would be
Adds the item to the basket. The label "Add" does not say what is added to where, and therefore we need an accessibility hint with the additional information.
Accessibility Label
- Accessibility Labels
-
Labels used to provide information about your app interface so everyone can use it.
Accessibility Labels provide metadata about your app, so that for example screen readers can access the elements in your app. They are critical for blind users, user with low vision, users with mobility disabilities and users with memory loss. Missing labels will make your app inaccessible for many users.
For some organizations, providing accessibility labels is mandatory, by law or by policy. In any case they are a good idea.
Apple has a video, Writing Great Accessibility Labels, which explains more.
API
- API
-
Application Programming Interface.
An Application Programming Interface is how a computer program talks to another computer program. A specific case is obviously services available on Internet. The computer that offers the API is a server and the program that uses the service is a client.
App administrator
- App administrator
-
A person with access to managing apps according to a Role.
Custom app
- Custom app
-
A customized app made available internally in your organization, or externally to specific, clients or partners.
Engage with businesses and educational institutions to design and build customized apps that meet the unique needs of their organization.
Custom apps are managed with Apple Business Manager and/or Apple School Manager.
The full Apple documentation for custom apps is available at https://developer.apple.com/custom-apps/.
App temple
- App template
-
An app made available to an organization as an model, example, guide or pattern to follow.
When you make an app available as a template, you are letting other people in your organization use it to make their own apps, based on the design, patchwork and data in the original app.
Making an app a template is a property of the app itself. If you delete the app, the template will also disappear. The apps created from the template will remain, though.
App version management
- App Version Management
-
Platform and tools to control what features and content is available to app users.
App Version Management is a platform architecture and set of tools that allow control over features and content that are made available to your users.
Component
Condition
- Condition
-
A unit of logic evaluating a number of keys according to a set of rules.
Conditions are used in several places, (most importantly in the if condition type of logic patch) to create a set of rules that generate a result based on a number of keys.
Condition group
Condition Key
- Key
-
A piece of data used by rules in a condition .
Keys are used in several places, (most importantly in the if condition type of logic patch) to store data to be used in rules to generate a result of
trueorfalse.
Operator
- Operator
-
A comparison or evaluation used in rules to compare two things (usually a keys and a value) or assert a statement.
(Relational) operators are used in used when creating rules in a condition, to give a result of
trueorfalse, by comparing two items, or by checking a property of a single item.Table 1. Relational Operators Operator
Meanin
Function
Comment
==Equals
Exact mathematical match.
!=Does not equal
Exact mathematical difference.
LikeInclusive word-match
Does the target contain the value?
Not likeExclusive word-match
Does the target not contain the value?
Different fromExact word-match
Not an exact match.
Is emptyKey has no value.
Is not emptyKey has any value.
<Lesser than
Number is lower than value.
<=Equal to or lesser than
Number is lower than value, or the same.
>Greater than
Number is higher than value.
>=Equal to or greater than
Number is higher than value, or the same.
BetweenIs the key within of the interval given by the values?
Not BetweenIs the key not within of the interval given by the values?
Remainder (%)Is the key evenly divisible with the value?
(Here % means modulo, not percentage.)
Examples:
-
In the rule
Age-(number) > 45, the operator verifies that the numberAgeis above45. -
In the rule
Name-(text) IS EMPTY, the operator checks if the text keyNamehas no value.
-
Rule
- Rule
-
An evaluation using an operator to compare a key to an expected value.
Rules are used in several places (most importantly in the if condition type of logic patch) to construct a piece of logic that evaluates a number of keys by using one or more operators, which results in a final value of
trueorfalse.Rules can be combined into groups to create even more complex logic structures.
Green |
A connection between Menu or View patches. |
Blue |
A connection that leads to or from a Logic Patch |
Red |
A connection where back navigation is blocked. |
Data
- Data
-
Information used by an app.
In Appspotr, the term data refers to stored information of various types that is used by an app.
D-U-N-S
- D-U-N-S number
-
Nine-digit company identifier assigned by Dun & Bradstreet
To publish apps with Apple as an organization, you must have a D-U-N-S Number. It consists of a nine-digit identification code. To get a D-U-N-S number you have to request it from Dun & Bradstreet.
D-U-N-S numbers are generally offered at no cost.
More information is available on the Apple Developer support site: https://developer.apple.com/support/D-U-N-S/.
Endpoint
- Endpoint
-
A web service message destination.
An endpoint is the address to a service, typically a target URL (including a port number, if applicable), which communicates with the network to provide its services.
For example, for the following URL:
the endpoint is
and the rest of the URL is paths and parameters to addess specific services and functions.
Event
- Event
-
A type of output that corresponds to something happening in the app
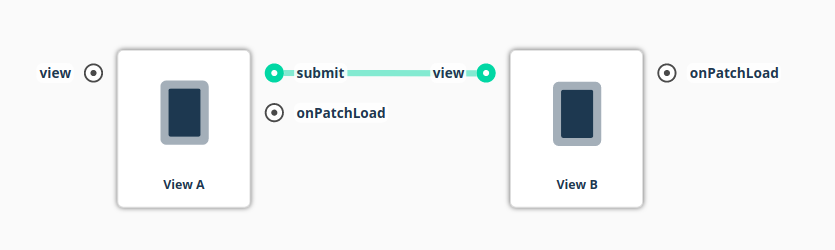
Events are a type of output that can be used to make things happen in the app. Typically, they are used navigate between views, but can just as well be used for any purpose you like.
For example, we have a
submitbutton in View A that when pressed opens View B:Here’s how it would look in Structure Builder:
File
- File
-
Downloadable documents.
Files can be uploaded and managed in the Assets tool in the App Editor.
Private app
- Private app
-
A customized app made available privately to organizations, clients or partners. (Also knowns as "custom apps").
Apps published through the Google Play Custom App Publishing API are private apps that cannot be made public.
The full Google documentation for private/custom apps is available at https://developers.google.com/android/work/play/custom-app-api.
Home patch
- Home Patch
-
The starting point of an app.
A view or navigation patch can be the home patch for an application. This makes that patch the starting point for the application when it is run.
The home patch is indicated by a house symbol in the top left corner of the patch.
HTTP/2
- HTTP/2
-
Improved protocol for communication on the Internet.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol 2 - HTTP/2 - HTTP/2 is a revision of the HTTP network protocol.
HTTP/2 uses the same methods, status codes, header fields, and URIs, as HTTP, but handles data frames and transport between client and the server differently.
The protocol promises increased request efficiency through minifying resources and performance gains through request prioritization, header compression and multiplexing.
HTTP/2 also allows servers to predict future requests and push data to the client beforehand.
HTTP
- HTTP
-
Protocol for communication on the Internet.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol - HTTP - is a protocol network for distributed, collaborative, and hypermedia communication, mainly on the Internet (World Wide Web).
It is used to exchange or transfer Hypertext - structured text using links between nodes containing text.
HTTP Body
- HTTP body
-
Content part of an HTTP request.
An HTTP body is a content part of an HTTP request or response message, containing the bulk of the content of the message.
The body may consist of: * Request line contining the HTTP and target (
GET /logo.gif HTTP/1.1* Response status line, such as (HTTP/1.1 200 OK`) * Additional HTTP Headers * An empty line * Optional data in different types (plain text, JSON, XML, form data, or multipart files and so on)
HTTP Status Codes
- HTTP status codes
-
Response codes for HTTP communication.
200
Number |
Code |
|
200 |
OK |
|
201 |
Created |
|
202 |
Accepted |
|
203 |
Non Authoritative Information |
|
204 |
No Content |
|
205 |
Reset Content |
|
206 |
Partial Content |
|
207 |
Multi-Status |
+
300
| Number | Code | |
|---|---|---|
300 |
Multiple Choices |
|
301 |
Moved permanently |
|
302 |
Moved Temporarily |
|
303 |
See Other |
|
304 |
Not Modified |
|
305 |
Use Proxy |
|
307 |
Temporary redirect |
+
400
| Number | Code | |
|---|---|---|
400 |
Bad Request |
|
401 |
Unauthorized |
|
402 |
Payment Required |
|
403 |
Forbidden |
|
404 |
Not Found |
|
405 |
Method Not Allowed |
|
406 |
Not Acceptable |
|
407 |
Proxy Authorization Required |
|
408 |
Request Timeout |
|
409 |
Conflict |
|
410 |
Gone |
|
411 |
Length Required |
|
412 |
Precondition Failed |
|
413 |
Request Too Long |
|
414 |
Request-URL Too Long |
|
415 |
Unsupported Media Type |
|
416 |
Requested Range Not Satisfiable |
|
417 |
Expectation Failed |
|
419 |
Insufficient Space On Resource |
|
420 |
Method Failure |
|
422 |
Unprocessable Entity |
|
423 |
Locked |
|
424 |
Failed Dependency |
+
500
| Number | Code | |
|---|---|---|
500 |
Internal Server Error |
|
501 |
Not Implemented |
|
502 |
Bad Gateway |
|
503 |
Service Unavailable |
|
504 |
Gateway Timeout |
|
505 |
HTTP Version Not Supported |
|
507 |
Insufficient Storage |
HTTP Header
- HTTP header
-
Leading part of an HTTP request.
HTTP headers are fields that can be transmitted as part of HTTP request or response messages. They provide additional parameters or information for the transaction being performed.
An HTTP header consists of a field name for identification and a value containing the data.
More information is available at https://www.iana.org
- HTTP Method
-
Type of HTTP request.
POST
Sends data to the service.
PUT
Replaces current representations with the content.
DELETE
Removes all current representations in the target URI.
HEAD
Retrieves status line and header section only from the service.
OPTIONS
Describes the communication options for the target.
TRACE
Performs a loopback test for the path to the target resource.
PATCH
Updates parts of the resource.
HTTPS
- HTTPS
-
Secure protocol for communication on the Internet.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure - HTTPS is a protocol for secure network communication, mainly on the Internet.
HTTPS consists of communication over Hypertext Transfer Protocol, using Transport Layer Security, or Secure Sockets Layer for encryption.
Icon
- Icon
-
Picture files for functional use in the app in an allowed format [TBD].
An icon is an image file small graphical representation of a program, feature, or file. When you click or double-click an icon, the associated file or program opens or an action is performed. For example, if you were to double-click My Computer icon, it would open Windows Explorer. Icons are a component of GUI operating systems, including Apple macOS X and Microsoft Windows.
Good icons are helpful to the user by being an understandable graphical symbol for the thing or action it represents.
Icons can be uploaded and managed in the Assets tool in the App Editor.
Image
- Image
-
A picture in an allowed image format.
Images can be used for any display purpose, such as background in a view, or as illustration in an article.
Images can be uploaded and managed in the Assets tool in the App Editor.
Image size
- Image size
-
Display size for images in views.
When using images, you can specify how they are displayed by choosing one of several options:
Option Description Comment coverResize the background image to cover the bakground.
The image may be stretched or cropped to fit.
containResize the background image to make sure the image is fully visible.
There may be space left over around the image.
stretchResize the image to cover the background, maintaining proportions.
repeatRepeat the image until it covers the background.
centerCenter the image in the view.
Does not change the image’s size.
Input
- Input
-
Incoming connection point for patches
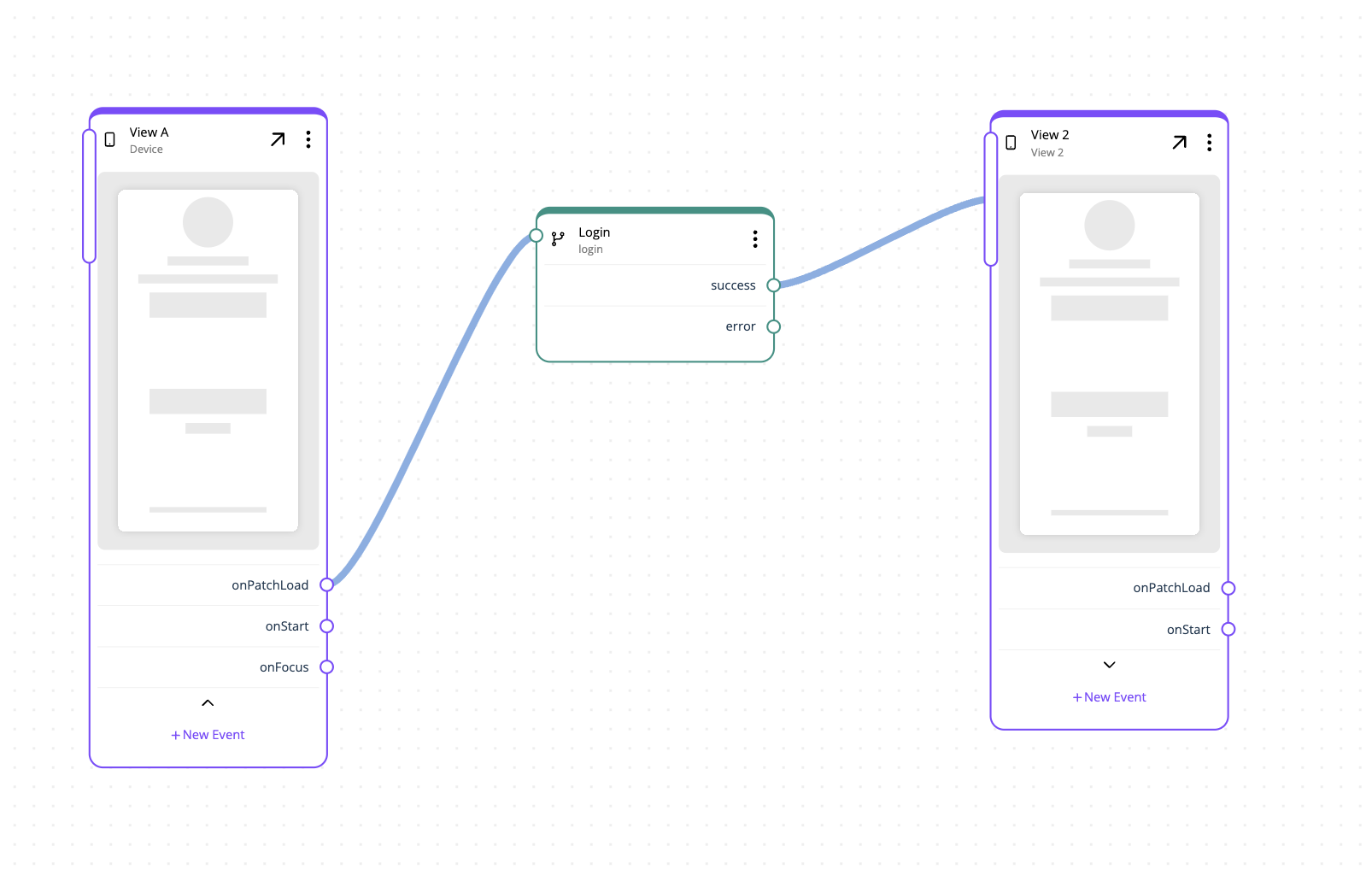
Inputs are connection points in a patches used to communicate or connect with other patches. Typically, they are used to transfer data, but can also be patches or navigation nodes. To be of any use, an input must connect to an corresponding output configured.
For example, let’s say we have a View *A that collects user input for
NameandMobilenumber. These values can be sent as outputs and used for display in View B, and simultaneously stored in a dataset.Here’s how it would look in Structure Builder:
Integration
- Integration
-
A connection to an external API using REST.
By setting up an Integration, you can connect your app to an external service or information store, to bring in data, by accessing an API using REST.
Authentication to the API is normally done via a HTTP header.
Base URL
- Integration base URL
-
The root address for an integration.
The integration base URL is the endpoint for making API calls to the service.
JSON
- JSON
-
JavaScript Object Notation - JSON - is a language independent data-interchange format.
It aims to be easy for humans to read and write while maintaining a strict structure to enable simple machine parsing and creation.
More information is available at http://www.json.org/
== Syntax
JSON consists of objects, consisting of a key and a value.
Keys must be strings, written with double quotes:
"Values must be one of the following:
-
an other JSON object
-
a double-quoted value:
-
a string
-
a number
-
an array
-
a boolean
-
null
== Example
json { "Config": { "Version": "V5.5-F", "configurationEnabled": "false", "pmaPort": "26401", "pmaNetworkProtocol": "2", "pmaRequestTimeoutSeconds": "60", "useHttpProxy": "false", "httpProxyPort": "0" } }
-
Logic group
- Logic group
-
Combined unit of logic blocks.
Logic groups are blocks consisting of multiple logic patches that work as small pieces of self-contained logic that create behavior in your app.
Logic groups are indicated by the logic group icon in patchwork.
To view the contents of a logic block, you can click the expand icon in the top left corner. This will show the connected logic blocks and allow you to further configure them.
Logic groups are generated dynamically, so they may change as you add or remove connections.
Logic patch
- Logic patch
-
App behavior and logic modules.
Logic patches are patches which provide various functions for your app related to working with logic, variables, states or data.
If you connect one or more logic patches together, they will automatically become a logic group.
Navigation
- Navigation
-
How a user can move through the features and views in an app.
Navigation in an app is the way a user can use the app, by using features and views, in effect moving through the app.
This structure can be created through drag-and-drop — without coding — by using patches and connections.
Navigation Patch
- Navigation patch
-
A patch containing a menu or submenu.
Navigation patches are using patches used to create menus, submenus and context menus in an app.
There are two types of navigation patches:
An app must contain at least one Main Menu, and can contain more than one for different views.
An app can contain several Sub Menus in different views.
Option type
- Option types
-
In many menus, you are able to select one of several types to in functions.
texttimenumberurlimagefilebooleanlocationlist
Organization
- Organization
-
An unit of organization for people and apps.
In Appspotr, the organization is a collection of people and the apps they create. It can represent a company, for instance a department or unit. An account with Appspotr can have one or more organizations associated with it.
It is best to think of it as a workspace where multiple can work together on creating apps.
Output
- Output
-
Outgoing connection point for patches
Outputs are connection points in a patches used to communicate or connect with other patches. Typically, they are used to transfer data, but can also be events or navigation nodes. In most cases, the receiving and must also have a corresponding input configured.
For example, let’s say we have a View A that collects user input for
NameandMobilenumber. These values can be sent as outputs and used for display in View B, and simultaneously stored in a dataset.Here’s how it would look in Structure Builder:

Patch
- Patch
-
Application logic, views and behavior.
Patches are nodes used to construct the application workflow, created with the Patchwork tool in the app editor.
Patches can be used with connections to create a navigation.
Patchwork
- Patchwork
-
App behavior, logic and navigation builder.
Patchwork is perhaps the most important tool in Appspotr 3. It is used to create the core of the application - the behavior.
By combining different views and logic-blocks to each other through patches, you can set up input and output properties, and the workflow of the application.
Permissions
- Permissions
-
The access granted to a role.
Permissions govern what you ara alllowed to do. Depending on the permissions you have, you will have access to different areas, and be allowed to do different things in those areas.
For app administrators in Appspotr 3, permissions are assigned to various roles, which users then can belong to in order to be granted those permissions.
In Appspotr 3 version 16, certain functions may require you to set permissions before you can use them. Some examples: Action Required permission Comment Add to dataset
Your group needs
createpermission on that specific dataset.Send push
You need
readaccess to the group you send the push to.Either be a member of the recipient group o have
readaccess to it.Add image to dataset
Your group also needs
createpermission on media.Push an image
Your group also needs
createpermission on media.As you can see, this may mean that you need to set multiple permissions before an action will work.
PWA
- PWA
-
Application software delivered through the web.
A progressive web application (PWA) is a type of application software delivered through the web, built using common web technologies including HTML, CSS and JavaScript. It is intended to work on any platform that uses a standards-compliant browser, including both desktop and mobile devices.
Since a progressive web app is a type of webpage or website known as a web application, they do not require separate bundling or distribution. Developers can just publish the web application online, ensure that it meets baseline "installability requirements", and users will be able to add the application to their home screen. Publishing the app to digital distribution systems like Apple App Store or Google Play is optional.
REST
- REST
-
A protocol for HTTP communication
REST - Representational State Transfer is a lightweight protocol for HTTP communication, where parameters are mostly encoded in the request URL.
Optionally, parameters can also be sent in the message body.
RESTful
- RESTful
-
A service with REST properties.
The term RESTful basically means the same as REST, but sometimes is used to mean web services that implement REST methods and architecture.
REST Method
- REST Method
-
Request type for accessing a resource.
A REST Method is an HTTP method used to access a resource.
REST Request
- REST Request
-
Request type for accessing a resource.
REST Requests are calls to a REST service.
REST Request can include HTTP Headers and parameters.
REST Resource
- REST Resource
-
Part of the URL identifying the accessible object.
A Resource is a part of the target URL, referring to the object to be accessed with REST methods.
For the URL
the resource is
` /maps/api/geocode/xml `
Role
- Roles
-
Collections of permissions to managing an app.
App Administrators can belong to different roles, which provides them with different levels of access to the app management.
Roles are created and configured for the organization, and can then be used in any apps belonging to it.
Some examples:
Admin — The admin roles gives access to all parts of the organization or app.
App Owner — An app owner can do everything related to the app including create new apps, publish apps and buy licenses.
Developer — A developer can do everything an app owner can do except buy new licenses and create new apps.
App Manager — An app manager can update content in datasets, media library, push notifications, app users, app admins and view analytics.
Designer — A designer can update content in datasets, media library, push notifications, view analytics and change the design.
Content Agent — A content agent can update content in datasets, media library and push notifications.
Member — A member has no cms access, but may be given access to various functions inside the app.
External — External users have no cms access to the app, and typicall have no special app access.
State
- State
-
Logical unit indicating the status of something.
A State is the current condition or status of an object or component. It can for example if a button has been turned on or off, if a view has been visited, a property has certain value, and so on.
Storage
- Storage
-
TBD
A Storage TBD
= Style :doctype: article :keywords: glossary, Style :description: glossary, Style
- Style
-
A design for the look and feel of an app that applies to all views and components.
A Style is the design that applies to the entire app and governs how it looks to the user. Think of it a s a template for views and components.
You can create multiple styles and select one as the current for the app.
Variable
- Variable
-
TBD
A Variable TBD
= Version :doctype: article :keywords: glossary, Version :description: glossary, Version
- Version
-
Development state for the software.
The version is a way to categorize the states and capabilites of software, indicated by a combination of numbers. It is a handy way to know which pieces of software will work with what other piece of software.
In Appspotr, you need to distinguish between Platform Version and the App Version. Also, the PWA version work slightly different from native apps.
App version
- App Version
-
The content available to an app.
The app version is the current state of an app. A few things get compiled into a version:
-
Patchwork
-
Views
-
Styles
-
Integrations
-
Storage
-
State
-
Variables
You should always include a title and description with a new version publish. Even if they can be for your own internal purposes they can also be made visible to the app users who receive teh updates.
It’s important to keep in mind that the entire contents of a version of app content are made public once they are published.
Do not put passwords or other data that is intended to be private in things that will be compiled into a version.
-
Platform version
- Platform Version
-
The underlying software that the apps and CMS are running on.
The platform version is the underlying code that the App and CMS are running on. It follows semantic versioning.
If your app is on Platform Version
0.16.1, the CMS will also be adapted for0.16.1.Given a Platform Version of
0.16.1, this is how those numbers are broken down:0
Major version
16
Minor version
1
Patch version
Changes to Major and Minor versions of Appspotr will include updates to your app that require you to run an app Update and rebuild for App Store & Play Store. Your users will have to update their apps to see new content and features made for this new Platform Version.
Patch updates will happen regularly for the latest Platform Version and will automatically be applied to all apps running on the affected Platform Version. Rebuilding for App Store & Play Store are optional, the apps will keeps themselves on the latest Patch version automatically. The benefit of rebuilding is that the starting Platform Version of the user’s app will be more up to date and not need to auto-update itself.
PWA version
- PWA Version
-
App version for PWAs.
All users who open the PWA will run that app at the latest version as long as there is app content available for that platform version.
+
If you are working with 0.16 and decide to update to 0.17, users will not get the updated PWA until you publish app content for this new version. This gives you control over when the actual update happens. You can check that any new behaviors or features fit the experience you would like your users to have.